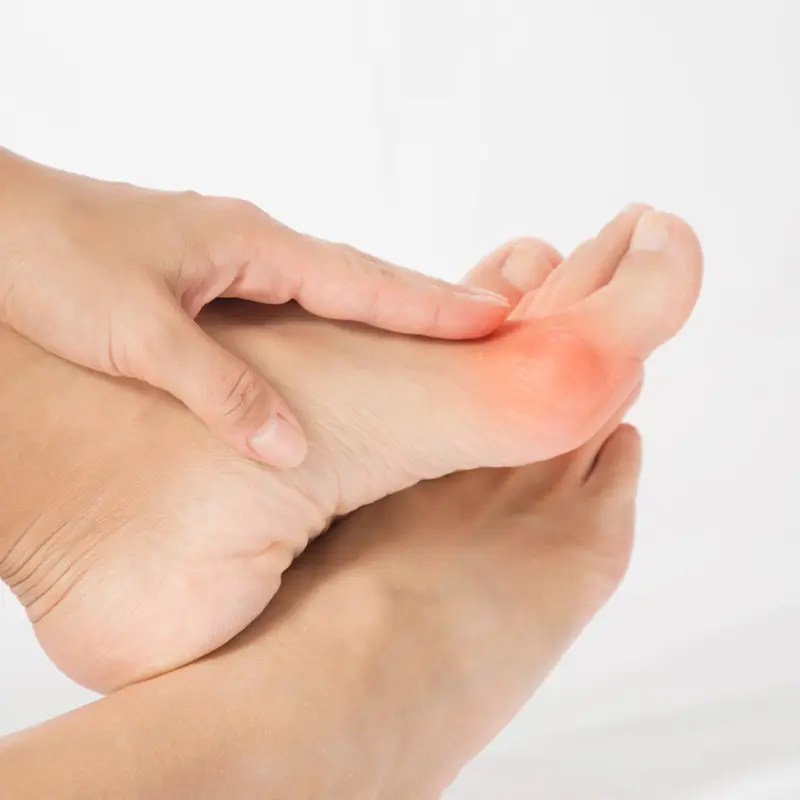
What is a Foot Deformity?
Foot deformities encompass a range of conditions that cause structural abnormalities in the foot. They can affect any part of the foot, including the toes, arches, or heel, and can lead to pain, discomfort, and difficulties in walking or wearing shoes.
What are common types of foot deformities?
- Bunions (Hallux Valgus)
- Hammertoes
- Claw Toes
- Flat Feet (Pes Planus)
- High Arch (Pes Cavus)
- Hallux Rigidus
Foot Deformity FAQ
For a proper diagnosis and recommended treatment plan,
we suggest you consult with a podiatrist for professional help and care.