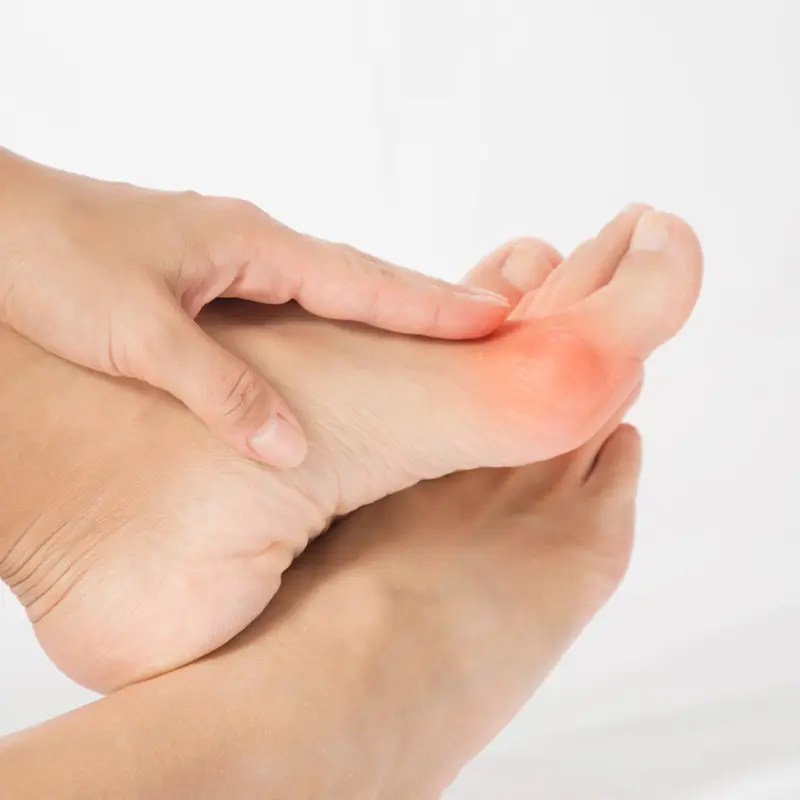
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by an excess of uric acid in the bloodstream. The high levels of uric acid lead to the formation of sharp, needle-like urate crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue, causing intense pain and inflammatory reactions. Gout typically affects one joint at a time and is known for its sudden, severe attacks that can wake a person from sleep.
What are the symptoms of gout?
- Intense joint pain, especially in the big toe
- Lingering discomfort after the most severe pain subsides
- Inflammation and redness — the affected joint or joints become swollen, tender, warm, and red
- Limited range of motion as gout progresses
Gout FAQ
For a proper diagnosis and recommended treatment plan,
we suggest you consult with a podiatrist for professional help and care.